Arbitrage trading is a strategy employed by investors and traders to capitalize on price variations among different securities or markets for potential profit.
What is Arbitrage Trading?

Arbitrage trading, which involves exploiting pricing differences or market inefficiencies to profit with minimal risk, is rooted in the principle that a well-functioning market should have consistent prices for the same asset, yet temporary disparities can arise due to factors like supply and demand imbalances, transaction expenses, or information disparities
How Does Arbitrage Trading Work?
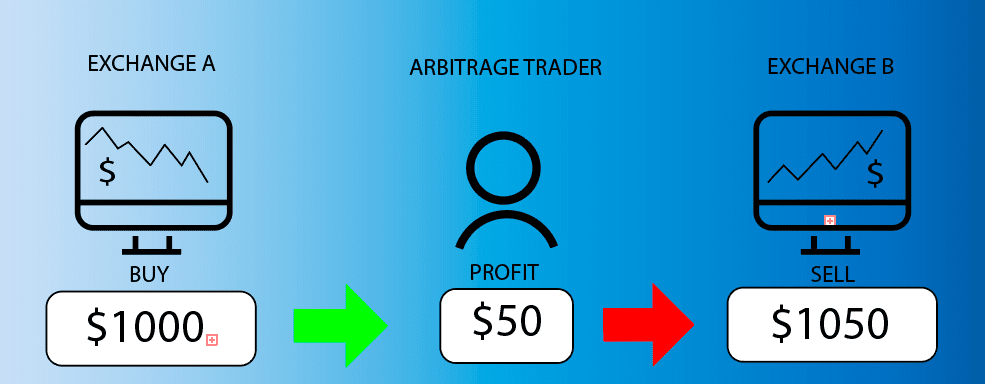
Arbitrage trading involves leveraging price inefficiencies or disparities in different markets or relevant assets to generate profits, with a primary focus on exploiting price discrepancies between markets. Traders in arbitrage typically buy a lower-priced asset in one market and sell it in another where it commands a higher price, necessitating swift identification of pricing differences across markets and agile execution. In this approach, profit primarily arises from price differentials rather than broader market trends. Success in arbitrage trading demands a deep understanding of the market, access to multiple markets, adaptability to changing market conditions, and effective execution and risk management strategies to navigate its intricacies.
Types of Arbitrage Trading
- Spatial Arbitrage: Spatial arbitrage is a strategy that capitalizes on price disparities between multiple markets or geographical areas. This can involve various assets, such as commodities or real estate, and requires efficient logistics to move goods between locations to capture profits.
- Temporal Arbitrage: Temporal arbitrage focuses on exploiting price discrepancies that evolve over time. This could involve trading securities within the same market but at different times of the day or capitalizing on futures contracts with varying expiration dates. Traders employing this strategy need to monitor and analyze the evolving market conditions to make timely and profitable trades.
- Merger Arbitrage: Merger arbitrage, often referred to as risk arbitrage, aims to profit from pricing differences that arise during corporate events like acquisitions or mergers.
- Dividend Arbitrage: Dividend arbitrage is a strategy that seeks to take advantage of price differences in dividend-paying equities. It typically involves trading options or related derivatives around the ex-dividend date, aiming to profit from changes in the stock’s price as it adjusts for the dividend payout.
- Risk-Free Interest Rate Arbitrage: This strategy exploits interest rate disparities between markets or countries. Arbitrageurs can borrow funds in a market with lower interest rates and invest them in a market with higher interest rates, capturing the difference as profit. This type of arbitrage usually involves low risk but requires careful consideration of exchange rate fluctuations and transaction costs.
- Statistical Arbitrage: Statistical arbitrage involves using quantitative models and statistical analysis to identify mispriced assets within a specific market or sector. Traders create portfolios of long and short positions based on historical relationships or statistical patterns, aiming to profit from the reversion to the mean or the continuation of certain price trends.
Advantages of Arbitrage Trading:
- Low Risk: Market-neutral approach minimizes exposure to overall market movements, enhancing stability.
- Consistent Returns: Capitalizes on temporary price discrepancies for steady, albeit modest, income.
- Market Efficiency: Aligns prices across markets, benefiting all participants.
- Diversification: Helps offset losses in other investments due to market neutrality.
- Liquidity: Involves highly liquid assets, reducing trading costs and enabling swift execution.
- Reduced Systemic Risk: Less vulnerable to broader market trends, advantageous in uncertain times.
- Profit in Any Direction: Can profit in both rising and falling markets.
- Risk Management: Utilizes techniques like stop-loss orders and hedging for capital protection.
- Capital Efficiency: Requires less capital compared to high-leverage strategies, making it accessible.
Disadvantages of Arbitrage Trading:
- Limited Profit Margins: Profit potential is often limited due to small price differentials.
- Execution Risks: Timing is critical, and delays in executing trades can erode profits.
- Transaction Costs: Trading costs, such as fees and spreads, can eat into profits.
- Technological Requirements: Requires advanced technology and access to multiple markets.
- Competitive Environment: Fierce competition among arbitrageurs can reduce opportunities.
- Market Volatility: Sudden price swings can disrupt arbitrage opportunities.
- Regulatory Constraints: Regulatory changes can impact arbitrage strategies.
- Risk of Model Errors: Statistical arbitrage relies on models, which can be flawed.
- Capital Lockup: Capital may be tied up in arbitrage positions, limiting flexibility.
- Market Liquidity: In illiquid markets, executing large arbitrage trades can be challenging.
Join our upcoming master class on Trading Potential on Monthly Expiry days to learn practically of the points discussed above.

Also, Check our Article on Zero to Hero Option Trading Strategy (80% ACCURACY) – 2023
Disclaimer: The information provided in this Blog is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Trading in the stock market involves a significant level of risk and can result in both profits and losses. Spider Software & Team does not guarantee any specific outcome or profit from the use of the information provided in this Blog. It is the sole responsibility of the viewer to evaluate their own financial situation and to make their own decisions regarding any investments or trading strategies based on their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Spider Software & Team shall not be liable for any loss or damage, including without limitation any indirect, special, incidental or consequential loss or damage, arising from or in connection with the use of this blog or any information contained herein.





