Option pricing is vital for trading. Options derive value from assets like stocks, and commodities. Factors like the Black-Scholes model, underlying assets, time, and volatility affect prices.
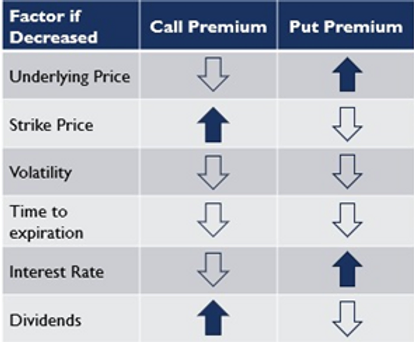
The Underlying Price
For call options:
- When the underlying asset price is higher than the option’s strike price (ITM – In The Money), the option has intrinsic value because you could exercise the option and immediately profit from the difference between the asset’s market price and the strike price.
- As the underlying asset price increases further above the strike price, the call option’s intrinsic value also increases, making the option more valuable.
For put options:
- When the underlying asset price is lower than the option’s strike price (ITM – In The Money), the put option has intrinsic value because you could exercise the option and immediately profit from the difference between the strike price and the asset’s market price.
- As the underlying asset price decreases further below the strike price, the put option’s intrinsic value increases, making the option more valuable.
The Strike Price
For call options:
- When the strike price is lower (closer to the current market price of the underlying asset), the call option allows the holder to buy the stock at a discounted price. This is known as an In The Money (ITM) call option.
- As the strike price decreases and becomes more favorable, the call option becomes more valuable because the holder can acquire the stock at a better price. Therefore, lower strike prices lead to more expensive call options.
For put options:
- When the strike price is higher (above the current market price of the underlying asset), the put option allows the holder to sell the stock at a higher price than the market price. This is known as an In The Money (ITM) put option.
- As the strike price increases and becomes more favorable, the put option becomes more valuable because the holder can sell the stock at a better price. Therefore, higher strike prices lead to more valuable put options.
Period before Expiry
- Call Options:
- As a call option holder, you benefit from a rising stock price. However, time works against you because the longer you hold the call option, the less time there is for the stock to make a substantial move above the strike price. As a result, the value of the call option decreases over time, especially if the stock price remains stagnant or does not rise significantly.
- Time decay accelerates as the expiration date approaches, leading to a more rapid decrease in the call option’s value.
- Put Options:
- As a put option holder, you benefit from a falling stock price. Similar to call options, time works against put option holders because the longer you hold the put option, the less time there is for the stock to make a substantial move below the strike price. Thus, the value of the put option decreases over time, especially if the stock price remains stable or does not decline significantly.
Time decay accelerates as the expiration date approaches, leading to a more rapid decrease in the put option’s value
Options Type
Call Option:
A Call option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) on or before the expiration date. Call options are typically used when the trader expects the price of the underlying asset to rise. If the underlying asset’s market price is higher than the strike price at expiration, the call option can be exercised profitably, enabling the trader to buy the asset at a discount.
Put Option:
A Put option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) on or before the expiration date. Put options are typically used when the trader expects the price of the underlying asset to fall. If the underlying asset’s market price is lower than the strike price at expiration, the put option can be exercised profitably, enabling the trader to sell the asset at a higher price than the market value.
Dividends
Impact on Call Option Premiums:
For call options, which give the holder the right to buy the underlying stock, a cash dividend reduces the chances of the stock price rising significantly. As a result, the potential for large gains from holding a call option diminishes. Consequently, call option holders are less likely to exercise their options when a dividend is imminent, which results in lower demand for these options. Lower demand leads to a decrease in call option premiums.
Impact on Put Option Premiums:
For put options, which give the holder the right to sell the underlying stock, a cash dividend can make owning the put option more attractive. The drop in the stock price due to the dividend means that put option holders can sell the stock at a higher price (the strike price) than the market price. This potential for higher profits increases the demand for put options, leading to higher put option premiums.
Volatility
Volatility and Option Prices:
It is a crucial factor that influences the price of options. It refers to the degree of variation or fluctuations in the price of an underlying asset, such as a stock. Higher volatility indicates more significant price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable price movements.
Impact on Option Prices:
Volatility has a significant impact on option prices. When the market is more volatile, options become more valuable because there is a higher probability of larger price swings, providing potential for substantial profits. As a result, options on highly volatile stocks are generally more expensive compared to those on less volatile stocks.
Interest Rate
Call Options:
Rising interest rates can have a positive effect on call option premiums. Higher interest rates may attract investors away from riskier assets (like stocks) and into safer assets (like bonds) with higher returns. As investors move away from stocks, the demand for call options may decrease, which could lead to a decrease in call option premiums.
Put Options:
On the other hand, rising interest rates may have a negative effect on put option premiums. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing money increases, which can lead to reduced business activity and potentially impact stock prices negatively. In such cases, the demand for put options may increase as investors seek protection against potential declines in the stock market, leading to an increase in put option premiums.
Learn how to Trade like a PRO on the Expiry Day. Click Here To Register

Also, if want to how Commodity & Currency Trading can be beneficial? Click here to Know
Disclaimer: The information provided in this Blog is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Trading in the stock market involves a significant level of risk and can result in both profits and losses. Spider Software & Team does not guarantee any specific outcome or profit from the use of the information provided in this Blog. It is the sole responsibility of the viewer to evaluate their own financial situation and to make their own decisions regarding any investments or trading strategies based on their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Spider Software & Team shall not be liable for any loss or damage, including without limitation any indirect, special, incidental or consequential loss or damage, arising from or in connection with the use of this blog or any information contained herein.





