The strike price in option trading also called the exercise price, is where a put or call option can be used. When choosing an option, investors or traders have two critical decisions to make: the strike price and the time until it expires. It significantly impacts the outcome of your option trade
Understanding the Strike Prices
The “strike price” is a crucial part of an options contract. It’s the price at which you can buy (if it’s a call option) or sell (if it’s a put option) the stock. Here are the basics:
When you start trading options, it’s like making a strategic bet on a stock’s future price:
Call Option: If you think the stock will go up, you can buy a “call” option. This gives you the right (but not the obligation) to buy the stock at a set price (strike price) before a certain date.
Put Option: If you expect the stock to drop, you can choose a “put” option. This provides the right (without the obligation) to sell the stock at the strike price before a specific date.
Role of Strike Price:
The strike price plays a big role. It’s your “deal price.” For instance, if you get a call option with a strike price of Rs. 100, you can buy the stock for Rs. 100, even if it’s worth more. And if you grab a put option at Rs. 90, you can sell the stock for Rs. 90, regardless of its current price.
Expiry Day Role:
The relationship between the strike price and the expiry day is crucial in options trading.
If you have a call option, you want the stock price to rise above the strike price before or on the expiry day. This way, you can buy the stock at a lower strike price and immediately sell it at the higher market price, making a profit.
Conversely, if you have a put option, you want the stock price to fall below the strike price before or on the expiry day. This allows you to sell the stock at the higher strike price and then buy it at the lower market price, also making a profit.
Impact of Expiry Day:
As the expiry day approaches, options can be influenced by various factors, including market conditions and the time left until expiration.
Time Decay:
Options are like perishable goods; their value erodes as time passes. This erosion is known as time decay, and it accelerates as the expiry day nears. The closer you get to expiry, the faster an option’s value can decline.
Volatility:
Market volatility, or how much and how quickly prices change, can affect options. Near expiry, options may react more significantly to sudden price swings.
Intrinsic vs. Time Value:
An option’s value is made up of intrinsic value (the profit you’d gain if you exercised the option immediately) and time value (the premium you pay for the time left until expiry). As expiry day approaches, time value diminishes, and intrinsic value becomes more critical.
Extra Note:
The choice of strike price matters. A lower strike price means your option has more intrinsic value as the stock rises, potentially leading to higher profits.
However, lower strike price options typically come with higher premiums, so there’s a trade-off between potential profit and the cost of the option.
As expiry day approaches, options can gain or lose intrinsic value depending on the stock’s price movement.
How to choose the Right Strike Price?
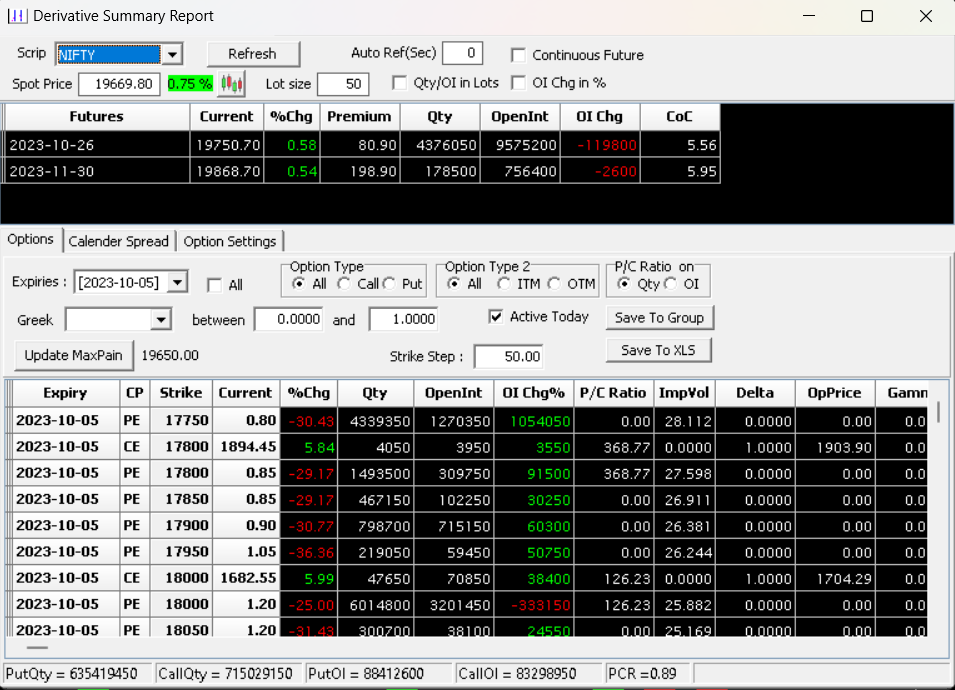
1. Assess Market Direction: Determine if you believe the stock’s price will go up or down. This helps you decide whether to choose a call option (if you expect it to rise) or a put option (if you expect it to fall).
2. Consider Current Stock Price: Look at the stock’s current market price. If it’s at Rs. 150, for example, you might consider strike prices around this range.
3. Analyze Volatility: If you expect the stock to have significant price swings, you might opt for a strike price farther from the current price. For lower volatility, choose a strike price closer to the current price.
4. Review Premium Costs: Lower strike prices usually have higher premium costs. Ensure the premium aligns with your budget and risk tolerance.
5. Match Expiry Date: Ensure the option’s expiry date matches your trading timeline. If you have a short-term view, choose a nearer expiration date; for long-term, go for a longer one.
6. Evaluate Overall Strategy: Consider your overall trading strategy. Are you aiming for quick gains, protecting investments, or something else? Your strike price should align with your strategy.
Remember, choosing the right strike price involves a balance between potential profit and cost, based on your market outlook and trading goals. It’s a skill that improves with experience.
Is the Strike Price the same as the Spot Price?
The strike price and spot price are not the same.
Spot Price:
This is the current market price of a financial instrument, like a stock or commodity, at that very moment.
Strike Price:
It’s a pre-decided price at which you can buy or sell the instrument in the future if you hold an option. The strike price is set when you enter an options contract, and it doesn’t change, unlike the spot price, which can fluctuate.
In short, the spot price is ‘now,’ and the strike price is ‘later.’
Bottom Line
Selecting the right strike price is a crucial choice for options investors and traders. It profoundly affects the potential profitability of an options position. Therefore, thorough research and analysis to determine the ideal strike price are essential steps to enhance your likelihood of success in options trading.
Learn about the Price Actions & take your Trading Skills to New Heights. By Clicking Here!
Also, Check our Article on Zero to Hero Option Trading Strategy (80% ACCURACY) – 2023
Disclaimer: The information provided in this Blog is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Trading in the stock market involves a significant level of risk and can result in both profits and losses. Spider Software & Team does not guarantee any specific outcome or profit from the use of the information provided in this Blog. It is the sole responsibility of the viewer to evaluate their own financial situation and to make their own decisions regarding any investments or trading strategies based on their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Spider Software & Team shall not be liable for any loss or damage, including without limitation any indirect, special, incidental or consequential loss or damage, arising from or in connection with the use of this blog or any information contained herein.






